The ChEESE CoE is a new initiative to integrate HPC and data across Solid Earth related disciplines in Europe. One of its main goals is to prepare ten flagship codes for exascale environments. These codes cover fields of study highly relevant for urgent computing, probabilistic hazard assessment and data science, such as computational seismology, magnetohydrodynamics, physical volcanology, and tsunami modeling.
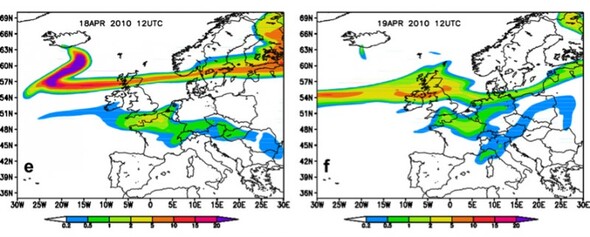
Simulation of the Eyjafjallajökull volcanic ash clouds using the Fall3d model
POP conducted performance assessments of all these codes at the start of the project and will do so again at the end. In this webinar, we looked in more detail at one of these, a physical volcanology code called Fall3D and explained how work conducted within ChEESE, aided by insights provided by the POP assessment, has led to a 10x improvement in scalability in a fairly short period of time.
The presentation slides are also available here.
| About the Presenters | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|

 Claudia Rosas has been a Post Doc in the Computer Applications for Science and Engineering department of Barcelona Supercomputing Center since 2016, with about 10 years’ experience in software engineering and performance analysis and optimization.
Claudia Rosas has been a Post Doc in the Computer Applications for Science and Engineering department of Barcelona Supercomputing Center since 2016, with about 10 years’ experience in software engineering and performance analysis and optimization. Mauricio Hanzich leads the Software Development group at the Computer Applications for Science and Engineering department of Barcelona Supercomputing Center. His main focus is software research and development for the oil industry, with broad experience in the development of HPC software for the whole stack, from the hardware to the application level.
Mauricio Hanzich leads the Software Development group at the Computer Applications for Science and Engineering department of Barcelona Supercomputing Center. His main focus is software research and development for the oil industry, with broad experience in the development of HPC software for the whole stack, from the hardware to the application level.